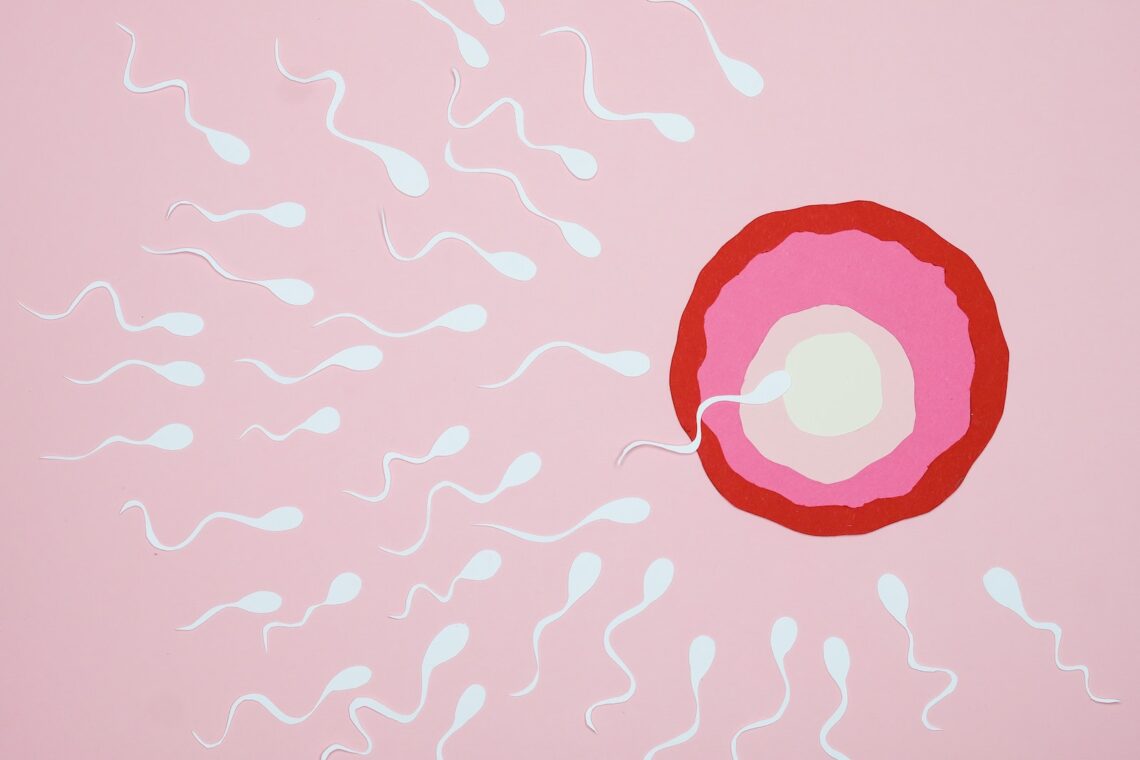
If you spend any time looking for fertility advice, you’ve likely heard that having sex every other day can increase your chances of conceiving. But why is that?
The NHS suggests that you have unprotected sex every other day throughout your menstrual cycle. This can increase your chances of conceiving during the fertile window.
Fertile window
Your fertile window is the time in your menstrual cycle when you’re most likely to get pregnant. It’s usually the five days leading up to ovulation, but can vary from month to month. Getting pregnant during this period is best, since the egg is more likely to be fertilized by sperm than at other times.
Identifying your fertile window can help you plan your sex life if you’re trying to conceive. It’s also important to remember that pregnancy depends on a combination of factors, and not just ovulation. That’s why it’s important to use backup birth control at all times.
While you may be able to predict your ovulation date using natural methods, like cervical mucus tracking or basal body temperature monitoring, these techniques aren’t foolproof. And, as we all know, women’s menstrual cycles can be very unpredictable.
A surge in luteinizing hormone (LH) triggers the release of an egg, which travels down the fallopian tubes to be fertilized by sperm. The fertile window is the six days before and after ovulation, but you can still become pregnant if you have sex outside of this time frame. It’s also important to keep in mind that sperm can live up to five days, so it’s possible to get pregnant even after ovulation has occurred. That’s why it’s essential to have sex every other day or more if you’re trying to conceive.
Sperm count
If you’re having trouble conceiving, it may be time to get a sperm count. The test will tell you how many sperm are in your semen and whether or not they are active. It can also help you understand why you’re having trouble getting pregnant. The test is simple and painless, so there’s no reason to wait!
You’ll need to provide a sample of your semen for the test. The doctor will then examine it under a microscope. They’ll look for a few things, including the number of sperm in the sample (sperm count) and how many of them are active (motility). They’ll also check the shape of your sperm (morphology). They’ll want to make sure that you have enough semen for the test, so they may ask you to provide two or three samples over a 3-month period.
A normal sperm count is about 48 million sperm per milliliter of semen. A low sperm count is less than 15 million sperm per milliliter of ejaculate. Other important factors include how motile the sperm are and how well they can travel to the egg.
Despite the decline in sperm counts, it’s important to remember that they don’t necessarily cause fertility problems. Instead, they might be masking other problems. For example, some men have a genetic condition that can reduce their sperm count and prevent them from becoming fertile.
Cervical mucus
Cervical mucus is the fluid that lines the cervix, vagina and vulva. It is responsible for lubricating, protecting the reproductive tract from pathogens and helping sperm swim to the egg. Its consistency changes just before an egg is released (ovulation) to make it more hospitable for sperm. The cervical mucus method, also known as the Billings Ovulation Calendar or the “fern test,” is based on monitoring the appearance of this fluid to determine when you are most fertile. This method works best if you have a regular menstrual cycle and are consistent with recording your mucus observations on a daily basis.
Sometimes called ovulation discharge or vaginal mucus, cervical mucus can look sticky, creamy, pasty, watery or stretchy. It is generally odorless and slippery to the touch. The amount and color of cervical mucus changes throughout the menstrual cycle as hormone levels rise and fall. It usually increases right before ovulation, becoming clear and white in appearance and resembling the texture of egg whites. This is the most fertile time for conceiving, and the perfect environment for sperm to move up to meet an egg. When the ovulation window closes, mucus will become thicker and less transparent. Avoid using douches or lubricants, which will change the consistency of cervical mucus and hinder your ability to use this method.
Stress
Stress can be a major barrier to pregnancy, especially for women who have trouble conceiving naturally. Fortunately, there are ways to reduce your stress levels and increase your chances of conception. These include exercise, getting enough sleep, and using fertility-friendly lubricants. These lubricants are designed to be compatible with sperm, so they won’t interfere with the natural sperm production process.
It’s important to note that sex every other day will only slightly increase your chances of conception, and that’s only if you’re having it during the fertile window. If you’re trying to conceive, it’s best to have sex in the morning after you get a good night’s rest. This will help your sperm count and improve the quality of your eggs.
Despite its negative connotation, stress is actually a necessary part of the human body’s survival mechanism. The body produces hormones during times of stress to respond to external pressure, including the physical and emotional stress caused by sex. Some of these hormones may affect ovulation and the formation of the uterine lining, but only during a specific ovulation cycle. However, it is still important to minimize stress during your ovulation cycle. For example, you should avoid consuming alcohol or smoking cigarettes while trying to conceive. It is also a good idea to avoid taking medications that are known to affect ovulation, such as steroids and birth control pills.